High cholesterol, also known as hypercholesterolemia, is a prevalent health condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It occurs when the levels of cholesterol in the blood exceed the recommended range, increasing the risk of developing various cardiovascular diseases. This comprehensive essay explores the causes and effects of high cholesterol, as well as its impact on overall health and well-being. Additionally, it discusses various methods of managing and preventing high cholesterol through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions.
- Introduction: Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in the cells of the human body. It plays a vital role in building healthy cell membranes and producing hormones, vitamin D, and bile acids to aid in the digestion of fats. However, an excessive amount of cholesterol in the bloodstream can lead to serious health complications, such as atherosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke. This essay delves into the factors that contribute to high cholesterol and the potential adverse effects it can have on an individual's health.
- Causes of High Cholesterol: Several factors contribute to high cholesterol levels in the blood. The primary contributors include:
2.1. Unhealthy Diet: Consuming foods high in saturated and trans fats, as well as cholesterol-rich foods like red meat, full-fat dairy products, and processed snacks, can significantly elevate cholesterol levels.
2.2. Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can lead to weight gain, which can raise LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, commonly known as "bad" cholesterol.
2.3. Genetics: In some cases, high cholesterol can be inherited from family members due to genetic mutations affecting cholesterol metabolism.
2.4. Age and Gender: As individuals age, cholesterol levels tend to rise, and men often have higher cholesterol levels than cholesterol in urdu.
- Effects of High Cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels in the blood can have severe consequences for overall health and well-being. Some of the effects include:
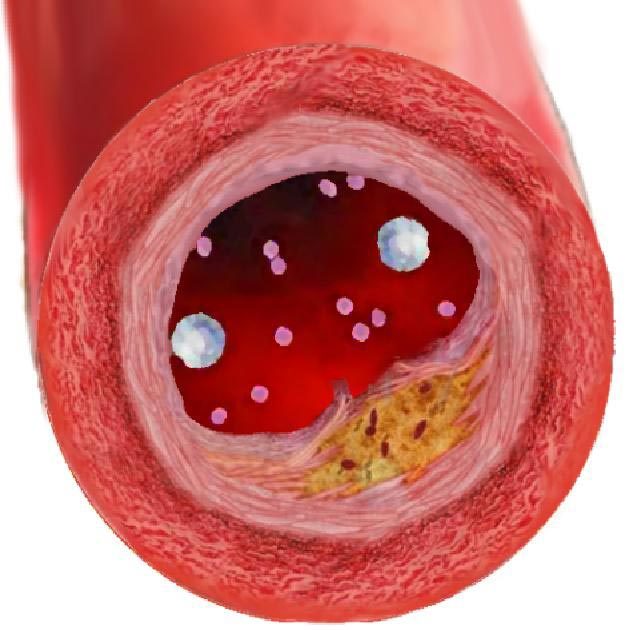
3.1. Atherosclerosis: High cholesterol leads to the accumulation of plaque in the arteries, narrowing and hardening them, a condition known as atherosclerosis. This restricts blood flow and increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
3.2. Coronary Heart Disease (CHD): The buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries can cause coronary heart disease, leading to chest pain (angina), heart attack, or even heart failure.
3.3. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): In PAD, cholesterol plaques restrict blood flow to the extremities, leading to leg pain and reduced mobility.
3.4. Stroke: If cholesterol plaque ruptures in the brain's arteries, it can cause a blood clot, leading to a stroke.
- Diagnosis of High Cholesterol: High cholesterol is typically diagnosed through a blood test called a lipid profile. The test measures the levels of total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, and triglycerides.
- Managing High Cholesterol: Managing high cholesterol involves a multi-faceted approach, which may include:
5.1. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Adopting a heart-healthy diet low in saturated and trans fats.
- Regular physical activity to improve cardiovascular health and maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
5.2. Medication: In cases where lifestyle changes alone are insufficient, healthcare professionals may prescribe statins or other lipid-lowering medications to manage cholesterol levels effectively.
5.3. Monitoring: Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to track cholesterol levels and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
- Prevention of High Cholesterol: Preventing high cholesterol is preferable to treating it. Some preventive measures include:
6.1. Healthy Diet: Incorporate more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into the diet while limiting saturated and Tran’s fats.
6.2. Regular Exercise: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
6.3. Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of high cholesterol and related cardiovascular complications.
6.4. Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake can positively impact cholesterol levels and overall health.
- Conclusion: High cholesterol is a significant health concern that can lead to severe cardiovascular diseases and reduce the quality of life. Understanding the causes, effects, and management strategies of high cholesterol is essential for individuals to make informed decisions about their health. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and seeking medical guidance when necessary, individuals can reduce their risk of high cholesterol and associated complications, promoting better long-term health and cholesterol kam karne ka tarika in urdu.




No comments:
Post a Comment